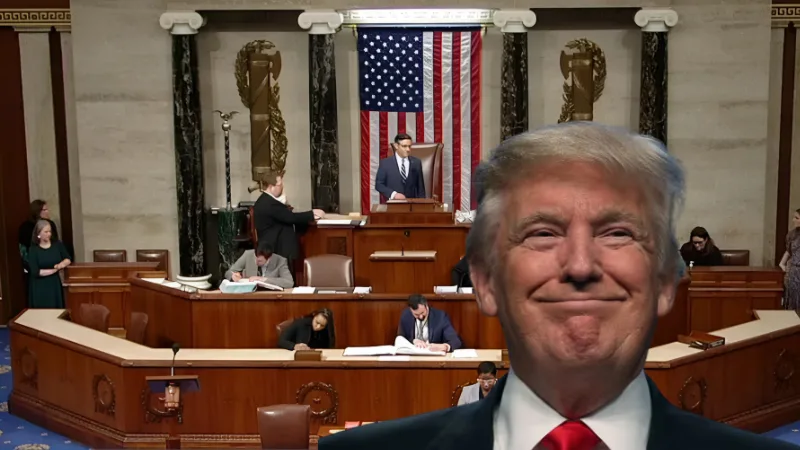
In a historic and deeply polarizing move, the U.S. House of Representatives has passed President Donald Trump’s signature economic and social legislation—the “One Big Beautiful Bill Act”—by a razor-thin margin of 215–214. The legislation now heads to the Senate, where the battle over its wide-reaching consequences for American taxpayers, healthcare recipients, investors, and the national debt is just beginning.
This 2025 legislative package combines sweeping tax reforms with significant cuts to social programs, expanded border enforcement funding, and new defense allocations. It’s being hailed by the Trump administration as a second-term economic reset—but critics warn it could leave millions of Americans uninsured and further balloon the national debt.
What’s in the Bill? Key Highlights for Taxpayers
1. Permanent Tax Cuts for Individuals and Families
The bill cements the 2017 Trump-era tax cuts that were set to expire at the end of this year. Key changes include:
- Standard deduction increase: Now $32,000 for married couples filing jointly (up from $27,700).
- Child tax credit: Boosted from $2,000 to $2,500 per qualifying child.
- Elimination of federal income taxes on tips and overtime wages, framed as a pro-worker reform aimed at restaurant and service industry employees.
These provisions are aimed at appealing to middle-class voters, although critics argue high-income households will benefit disproportionately due to parallel reductions in capital gains and estate taxes.
2. SALT Deduction Expansion
One notable shift comes in the treatment of State and Local Tax (SALT) deductions. The cap will rise from $10,000 to $30,000 for most households—though the expanded deduction phases out for single filers earning over $200,000 and joint filers earning over $400,000.
This change is seen as a political concession to lawmakers from high-tax states like New York and California, where prior SALT caps drew bipartisan criticism.
Medicaid, SNAP, and Social Safety Net Overhaul
While tax cuts are grabbing headlines, it’s the bill’s social program cuts that have ignited the most controversy.
3. Medicaid Work Requirements and Reductions
The legislation imposes an 80-hour monthly work requirement for able-bodied adults without dependents receiving Medicaid. This provision takes effect in December 2026.
The Congressional Budget Office (CBO) projects that up to 13.7 million people could lose Medicaid coverage over the next decade as a result of this change, many due to paperwork burdens and state enforcement inconsistencies rather than true ineligibility.
Additionally, the bill slashes nearly $800 billion from Medicaid over 10 years, a major offset used to finance the tax cuts.
4. SNAP (Food Stamps) Cuts
Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP) funding faces a multi-billion-dollar cut. New eligibility verification rules and shorter recertification periods are expected to reduce enrollment by approximately 2.1 million households over five years.
Supporters argue the reforms will curb fraud and encourage workforce participation. Detractors call it a direct hit on working-poor families during a period of high food inflation.
Big Money for Border and Defense
A core theme of Trump’s bill is “national strength,” underscored by a surge in defense and border enforcement funding.
5. Border Wall Completion and Deportation Surge
- $50 billion allocated to complete the U.S.-Mexico border wall.
- $8 billion earmarked for hiring nearly 20,000 new immigration and border patrol officers.
- $48 billion will fund the construction and expansion of detention centers.
- The Department of Homeland Security will receive new authority to deport up to 1 million individuals annually, a massive ramp-up from prior benchmarks.
These provisions resonate with Trump’s base and fulfill a top-line campaign promise from 2020 and 2024. Immigration advocates and human rights groups are already preparing court challenges.
6. Defense Spending Hits $1 Trillion
For the first time, the U.S. defense budget will cross the $1 trillion threshold, with an additional $150 billion funding bump. Key initiatives include:
- Development of the “Golden Dome” missile defense system, inspired by Israel’s Iron Dome.
- Expansion of cyber warfare capabilities.
- Increased troop pay and modernization of naval and aerial fleets.
This aligns with Trump’s stated goal to restore “military dominance and deterrence.”
Energy & Green Incentive Rollbacks
As part of broader deregulation efforts, the bill repeals several green energy subsidies put in place by the Biden administration, including:
- Tax credits for residential solar installations.
- Incentives for electric vehicle (EV) purchases.
- Federal support for battery storage technology.
These incentives will be phased out by 2028.
Investors in green tech could feel the pinch as markets reassess growth expectations. Traditional energy stocks—particularly fossil fuels and defense contractors—may benefit from the shift.
Economic Fallout: Debt, Deficits, and Credit Warnings
While the White House claims the bill will “supercharge” the economy, fiscal watchdogs and credit rating agencies are flashing red.
7. Moody’s Downgrade
Following the bill’s passage in the House, Moody’s downgraded the U.S. credit rating, citing a projected rise in the national debt to 134% of GDP by 2035.
Critics say the bill’s $4 trillion price tag over a decade is fiscally reckless, especially with rising interest costs and an aging population.
“This is not tax reform; it’s tax recklessness,” said Maya MacGuineas, president of the Committee for a Responsible Federal Budget.
Political Blowback and What’s Next
The bill’s journey to law is far from over. It now heads to the Senate, where Republicans hold a narrow 53–47 majority. But some moderate GOP senators have voiced concerns over the bill’s Medicaid changes and deficit impact.
Senator Josh Hawley (R-MO) warned that cutting healthcare for the working poor is “morally wrong and politically suicidal,” suggesting revisions are likely before a final vote.
Senate debate is expected to begin in early June, with the Trump administration pushing for final passage before the July 4 recess.
What Investors Need to Watch
If passed, this bill will shift the landscape across multiple sectors. Here’s how investors can prepare:
- Defense stocks: Names like Lockheed Martin (LMT), Raytheon (RTX), and Northrop Grumman (NOC) are poised to benefit from record Pentagon funding.
- Private prison and border contractors: Companies such as GEO Group (GEO) and CoreCivic (CXW) could see revenue upside from increased detention capacity and immigration enforcement.
- Energy sector: Traditional oil and gas plays may gain from the rollback of green incentives. Watch names like ExxonMobil (XOM), Chevron (CVX), and Halliburton (HAL).
- Healthcare insurers and hospitals: Potential Medicaid enrollment drops could hurt managed care companies like Centene (CNC) and Molina (MOH).
Also, increased deficits and Moody’s downgrade could add pressure to Treasury yields and U.S. borrowing costs—making bond markets worth watching closely.
One Big Beautiful Bill
The “One Big Beautiful Bill Act” is arguably the boldest piece of economic legislation since the Reagan tax cuts of the 1980s. It represents a seismic shift in America’s fiscal priorities—tilting power back toward defense, border security, and deregulation while reducing the scope of the welfare state.
Whether this vision for the American economy will create lasting growth or deepen the inequality and debt burden is the next debate—one now heading to the U.S. Senate.